Treatment

Treatment can only be as good as previous diagnostics. Only if the correct injury pattern as well as the cause of the injury has been identifiedan optimal treatment can be established.
The decision to treat without or with surgery depends on several factors. The most important factors are the degree and extent of surgery as well as the sport activity.
Non-surgical treatment

In the early phase after injury the physiotherapy aims to calm down the knee joint and reduce the pain and swelling.
In the next phase, if treated non-surgically, physiotherapy aims for proprioceptive and muscle training to strengthen the knee joint.
Surgical treatment
Suture of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
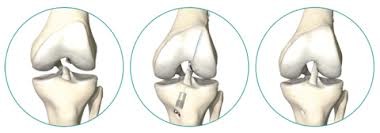
Suturing of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is possible in the early days (first 3 weeks) after ACL tear. Not every ACL need to be reconstructed.For patients with certain ACL tears the ACL can be sutured and healed without a transplant.
The most important clinical benefit is that for ACL reconstruction a tendon or ligament of the patient has to be harvested as transplant, which comes along with some donor site morbidity. This is not necessary, when the ACL can be healed.
For suture of the ACL different systems are available today. One of those is LIGAMYS, Mathys, Bettlach, Switzerland. We are proud to offer you this method for healing of your ACL.
Reconstruction of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
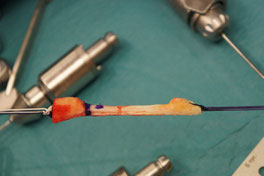
Reconstruction of ACL should be performed in all patients, who complain about instability symptoms such as giving way. In all others an ACL tear can be treated non-surgically with intensive physiotherapy and rehabilitation.
The optimal timing for ACL reconstruction is when the knee swelling and pain has resolved after ACl tear. This is typically the case about 4-6 weeks after ACL injury.
Several different grafts such patellar tendon, hamstring tenonds or quadriceps tendon are typically used as transplants. These are harvested from the same knee joint.
The ACL grafts are introduced into the thigh and shin bone through bone tunnels. Fixation of the grafts in the tunnel are achieved by screws, buttons, or press-fit.
Reconstruction of posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
The posterior cruciate ligament can also be reconstructed. in our experience we use the quadriceps tendon in arthroscopic inlay technique.
Here you find an image of a knee with a ruptured PCL and posterior instability.
Meniscal surgery
It is the primary aim to preserve as much meniscus as possible.
A partial meniscectomy is only necessary, when a suture of the meniscus has no chance of healing. This can be due to reduced meniscus tissue quality. In addition, the time from injury is essential. The more time has passed from injury the lower the success rate of meniscus suturing.
Some patients experience pain after partial or subtotal meniscectomy. In these cases a partial or total meniscus substitution or transplantation can be clinically sound. For meniscal substitution a collagen meniscus or synthetic meniscus can be used. For a meniscus transplantation typically allografts are used.
Cartilage repair and reconstruction
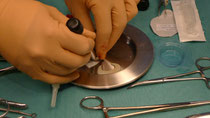
Microfracturing is the most frequently performed surgery in patients with cartilages lesions. For microfracturing the remaining surface cartilage layer is removed and small holes are made into the subchondral bone. Bleeding from the subchondral bone leads to invasion of stem cells and restoration of a cartilage like layer.
In matrix associated cartilage repair procedures cell free implants, typically consisting of collagen, are implanted into the cartilage defect. A cartilage like layer is restored.
For autologous chondrocyte transplantation cartilage cells are harvested, which are then enhanced in vitro. In a second surgery the cells are then implanted in the cartilage defect.
Surgery for patellar instability
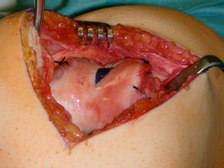
For treatment of patellofemoral instability a variety of treatment options exist. It is important to perform the at least invasive surgical procedure.
The most commonly used surgical methods are: reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL reconstruction), trochleoplasty

 Ihr Kniespezialist in Basel
www.kniedoktor.ch
Your English speaking Chirurgie du genou specialise
knee expert in Basel! expert a Bale
www.kneesurgeon.ch www.kneedoctor.ch
Ihr Kniespezialist in Basel
www.kniedoktor.ch
Your English speaking Chirurgie du genou specialise
knee expert in Basel! expert a Bale
www.kneesurgeon.ch www.kneedoctor.ch